The following is a guest post from Sunbelt Rentals, Inc.
When a municipality puts out an RFQ for an engineering project and includes the following words—design a temporary sanitary sewer bypass system as needed to construct improvements—design engineers need to focus on two tasks: defining the scope and designing the solution. But typically, sewer bypass is just one part of a much larger project, and often design engineers aren’t trained in sewer bypass design. Fortunately, you can ask for help from bypass subcontractors and rental companies. That way, when your engineering firm helps the municipality take the project out for bid, estimators will be working with solid information that will help ensure reasonable bids.
The goal is to scope and design quickly, accurately, and effectively to avoid expensive mistakes and delays. Read on for a how-to guide to help you get it right.
Define the Scope
Before listing the steps to define the scope, let’s define what project scope actually means.
Projects are time-constrained undertakings to produce a product, service, or result. The scope defines the purpose, the ultimate goal, and how you will achieve it. Scope also determines the boundaries—what’s included in the project and what’s not. If you fail to define scope adequately, your project will likely end up over budget and behind schedule.
According to the Project Management Institute, scope changes are the single biggest reason projects fail. If the scope becomes a moving target, you’re increasing the chance for the project and your career to take a nosedive.
Here are six steps to help you thoroughly define the project scope.
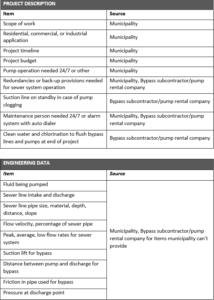
- Provide an overall project description. The project description should include what the municipality wants to accomplish, the current sewer capacity, equipment in use, location and layout of existing facilities, and duration of the project. You may also want to note challenges, such as existing buildings, roads, and other structures, or areas of environmental concern such as creek crossings.
- Explain the driving forces. Billions of dollars in federal aid have been made available to rehabilitate decaying sewer systems. Many municipalities have taken advantage of the funds to initiate rehabilitation projects, whether for sewer lines, lift stations, or wastewater treatment plants. Or the municipality may be working under a consent decree that mandates specific improvements to a sewer system by a deadline.
- Specify the deliverables. The municipality’s requirements may list the details of sewer system improvements. But often the sewer bypass system itself simply directs you to design a system that will allow the improvements to be made without an interruption of service. It’s up to you to determine the requirements and provide the specifications.
- Determine the boundaries. Based on the improvements the municipality intends to make, you’ll need to determine exactly what the sanitary sewer bypass system should look like to meet the sewer requirements for as long as the project is active. For example, you’ll need to determine if the temporary system must operate at all times during construction, if it can be tied into the existing sanitary sewer system overnight, if the existing sanitary sewer system can be returned to normal flow for long periods, and if the flow can be partially diverted or must be fully diverted.
- State your assumptions. Define the conditions you’re assuming and their impact on the project. For example, the municipality may claim sandy soil in an area. If it’s actually rocky, you’ll be less productive while dealing with unexpected soil conditions. That will impact project time and cost, and generate a change order.
- List uncertainties and potential impacts. Uncertainties create risk and cost money. For example, you need to know up front of any time limitations on when work can be performed to complete the project. You also need to be aware of physical obstructions such as rivers and streams, railroad crossings, parks, and public and private property the sewer bypass may need to cross.
Design the Solution
Your bypass system design needs to be as detailed as possible, or you risk change orders, higher costs, and a damaged reputation. You may want to rely on a bypass subcontractor and/or rental company to help you specify accurately. In addition, technology continues to evolve, and the design should allow the project to meet the highest standards at the lowest cost in the shortest amount of time.
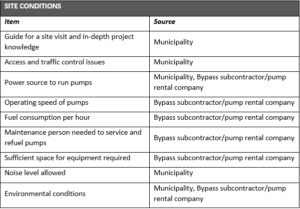
If you’ve established a partnership with a company with expertise in designing sewer bypass systems, you’re a step ahead. You can provide the known parameters to the bypass subcontractor or pump rental company and receive a sewer bypass design in return. For parameters that the municipality can’t provide, your partner can go on site and fill in missing pieces of engineering data to ensure the designed system will operate as intended. A bypass subcontractor will typically provide you with a quote up front, but you normally won’t receive the engineering submittal until after you sign a contract. The engineering submittal and drawings should show exactly how they’ll perform the project and what assumptions they’ve used to make calculations. You can take that back to the municipality for confirmation.
To keep your plans for a sewer bypass on point, here’s a list of the key requirements and where you can get the information to specify them.
We hope this guide will help you better define the scope and design the solution for sewer bypass projects. But you don’t have to go it alone. It helps to work with a partner that can not only provide high-quality equipment and accessories, but engineering knowledge and installation expertise.
Interested in learning more? Join Sunbelt Rentals for a free webinar with Trenchless Technology on August 15, 2019 at 2 pm EST. Register here